
Opinions expressed here are ours alone, and are not provided, endorsed, or approved by any issuer. Our articles follow strict editorial guidelines and are updated regularly.
The average daily balance on a credit card is how much you owe daily, on average, over a billing cycle. Credit card companies use this average to determine the amount of interest you pay if you carry a balance from month to month.
A billing cycle is the period between the last statement’s closing date and the next. For credit cards, this is usually about one month. During this time, the issuer records and adds all of the transactions you make with your credit card to your account.
At the end of the billing cycle, the credit card company sends you a statement that shows all the charges, payments, interest, fees, and other transactions that occurred during that period, along with the total amount you owe.
-
Navigate This Article:
How the Average Daily Balance is Calculated
Here’s a detailed explanation of how to calculate the average daily balance (ADB) for a credit card, including the formula and a step-by-step example:
Formula
The formula for calculating the average daily balance (ADB) is:
ADB = Sum of Daily Balances / Number of Days in the Billing Cycle
Steps to Calculate ADB
These are the steps a credit card issuer follows to calculate ADB. You can follow these same steps to verify the credit card issuer’s numbers:
- Track daily balances: Keep a record of the balance on your credit card at the end of each day. This includes any purchases, payments, or other charges added or subtracted from your balance.
- Sum up daily balances: Add all the daily balances together.
- Divide by the number of days: Take the sum from Step 2 and divide it by the total number of days in the billing cycle.
Example
Suppose your Billing Cycle is 30 days long, and you start with a balance of $0. Here’s how the balance evolves:
- Day 1-10: You have a balance of $100 (maybe you made a purchase of $100 on the first day.
- Day 11: You pay off $50, reducing the balance to $50.
- Day 12-20: Balance remains at $50.
- Day 21: You make another purchase of $200, increasing the balance to $250.
- Day 22-30: Balance remains at $250.
Step 1: Calculate the sum of daily balances:
- Days 1-10: 10 days × $100 = $1,000
- Days 11-20: 10 days × $50 = $500
- Days 21-30: 10 days × $250 = $2,500
Total sum of daily balances = $1,000 + $500 + $2,500 = $4,000
Step 2: Calculate the Average Daily Balance:
ADB = $4,000 / 30 days = $133.33 per day
This $133.33 is the average amount you owe each day during this billing cycle. Your interest for the month would be calculated based on this average balance. You would only owe interest if you did not pay the entire balance by the payment due date.
Average Daily Balance Determines Interest Charges
The ADB is an important factor for credit card users. It directly influences the amount of interest you may incur if you carry a balance from one billing cycle to the next. Understanding ADB can help you manage your payments and take steps to avoid interest charges.
A Higher ADP = More Interest
Credit card companies use the ADB to calculate the interest charges on your account. A higher average balance during the billing cycle will lead to higher interest charges. You can lower your ADB and interest expenses by managing your daily balance, as we explain below.

To calculate the interest charges on a credit card, you first need to understand the annual percentage rate (APR). The APR is the yearly rate of interest. You can convert it into a daily periodic rate of interest, which is what credit cards typically do when they use daily compounding.
Formulas for Interest Calculation
We need to calculate the Daily Period Rate first.
- Daily periodic rate (DPR): This formula divides the APR by 365 days to find the daily interest rate:
DPR = APR / 365
- Interest for the billing cycle: This multiplies the ADB by the DPR and the number of days in the billing cycle:
Interest = ADB × DPR × Days in Billing Cycle
Example
Let’s use the earlier example where the average daily balance for the 30-day billing cycle was $133.33. Assume the APR on the credit card is 24.99%:
Step 1: Calculate the Daily Periodic Rate:
DPR = 24.99% / 365 days ≈ 0.06847%/day
Step 2: Calculate the Interest for the 30-Day Cycle:
Interest = $133.33 × 0.0006847/day × 30 days = $2.74
This calculation shows how APR, daily balances, and transaction and payment timing determine credit card interest.
Billing Cycle Implications
The length of the billing cycle and timing of purchases are crucial factors when you calculate the potential interest charges on your credit card. Here’s an explanation of these factors:
- Length of the billing cycle: The number of days in the billing cycle affects how much each day’s balance matters when figuring out your average balance. If the billing cycle is long, each day’s balance counts a bit less towards the average. If it’s short, each day’s balance counts more. So, if you have a high balance for just a few days in a long cycle, it won’t affect your average balance as much as it would in a shorter cycle.
- Timing of Transactions: Your average balance can change when you buy things or pay off some of your balance during the billing cycle. If you buy something expensive at the start of the cycle, it will raise your balance for more days than if you purchased it at the end of the cycle. Also, paying off some of your balance early in the cycle helps lower your average balance more than if you pay later.
- Timing of the billing cycle start: The billing cycle start and end dates can also affect your average balance. This is especially true if you usually charge purchases or make a credit card payment around the same time each month. If the cycle begins right after you typically make a big purchase or make a credit card payment, it will affect your average balance differently than if the cycle starts before you do these things.
Knowing how these factors influence your interest can help you time your purchases and payments to reduce your interest charges.
The Role of the Grace Period
The grace period on a credit card is the time between the end of a billing cycle and the date by which you must pay your balance in full to avoid paying interest on new purchases (i.e., the payment due date). This period usually ranges from about 21 to 25 days, depending on the credit card issuer.
Virtually all credit cards offer a grace period, but a few don’t. Always check the cardmember agreement to verify the length of a card’s grace period.
You will avoid interest charges as long as you pay your entire purchase balance each month before the end of the grace period. This means that the grace period allows you to borrow money without any cost, provided you clear your balance in full and on time.
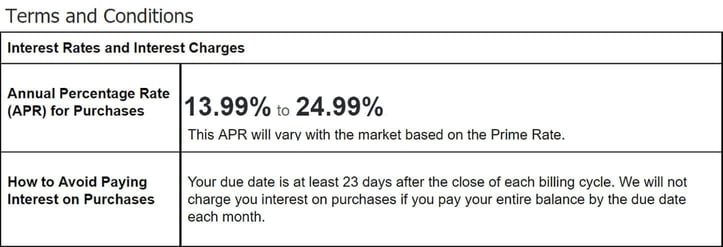
You lose the grace period benefit if you carry a balance from one billing cycle to the next. New purchases will start accruing interest at once without any interest-free days. To regain the grace period, you need to pay off the entire outstanding balance, including any amount carried over, by the payment due date.
The grace period does not apply to cash advances or balance transfers. Interest on these types of transactions accrues immediately.
How it Differs From Other Calculation Methods
The average daily balance method is the standard the credit card industry. Still, other methods also exist, including the daily balance method and the previous balance method:
- Average daily balance (ADB): This is the most widely used method among credit card issuers because it fairly represents your actual credit usage over the billing cycle.
- Daily balance method: This method is less popular than the Average Daily Balance Method. It could make you pay more interest because it charges interest on your card’s balance every single day, not using an average.
- Previous balance method: This is the least used method because it is the most unfair. It calculates interest on what you owed at the end of the last billing cycle, ignoring any payments you made during the month. Because of that, most credit card companies don’t use it.
Here is a chart contrasting the average daily balance method with the daily balance method and the previous balance method:
| METHOD | DESCRIPTION | IMPACT OF PAYMENTS | SUITABILITY |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Daily Balance (ADB) | Calculates interest by averaging the balances recorded each day over the billing cycle. | Payments reduce the balance for later days, lowering the average balance and potential interest. | Suitable for those who carry a balance and make regular payments throughout the billing period. |
| Daily Balance Method | Calculates interest by applying the daily interest rate to each day’s full balance, then summing up. | Payments immediately lower the balance and reduce the interest for subsequent days. | It helps those who pay off their balances quickly after making new charges. |
| Previous Balance Method | It calculates interest based on the balance at the end of the previous billing cycle, regardless of changes during the current cycle. | Payments do not affect interest charges in the current cycle, as they hinge on the previous cycle’s ending balance. | It may not reflect current spending or payment habits, which is potentially unfair to those who pay off their balance. |
To sum up, card issuers favor the average daily balance method due to its fairness and accuracy in how you use credit throughout the entire billing cycle. Issuers use the daily balance method less often and seldom employ the previous balance method.
Factors that Influence the Average Daily Balance
The average daily balance is a way to figure out how much you owe your credit card on average during the billing cycle. What you buy, when you pay, and other charges can all change this average. Understanding these factors can help you manage your credit card better.
Purchases
Every time you use your credit card to buy something, your average balance can increase. Your average will be higher throughout the month if you make a big purchase at the start of the billing cycle because the purchase affects your balance each day until you pay it off.
Payments
When you pay your credit card bill also matters. Paying early in the billing cycle reduces your balance sooner, as this lowers your average balance.
But your average balance will stay higher for longer if you wait until the end of the cycle to make a payment.
Withdrawals and Other Charges
Taking out cash with your credit card, along with fees (e.g., late payment fees or annual fees), adds to your balance. Unlike purchases, which usually have a grace period, cash advances start accruing interest right away.
On your credit card statement, you will see different balances for purchases and cash advances. The statement separates these because they can have different interest rates and terms. The interest rate for cash withdrawals is often higher than for purchases and applies immediately.
Strategies to Minimize Your Average Daily Balance
Keeping your average daily balance low reduces the amount of interest you pay. Here are a few straightforward strategies that can help you achieve this.
Making Multiple Payments
By paying weekly or biweekly, you lower your balance more quickly, reducing the ADB and, therefore, lowering interest charges.
| The Effects of Making Multiple Payments |
|---|
| 1. Lowers your balance more quickly. |
| 2. Reduces your average daily balance. |
| 3. Lowers interest charges. |
This method makes sense if you get paid (and make payments) multiple times each month.
Avoiding New Purchases
Try to control your spending to keep your ADB low. Avoid new purchases with your credit card, especially for non-essential items, while you’re already carrying a balance.
Use a debit card or cash instead for essential spending. This prevents your credit card balance from growing and keeps your ADB lower, thereby reducing the interest you accrue.
Using Introductory 0% APR Offers
Many credit cards offer new card members an introductory 0% APR on purchases for a certain period after opening an account. You can carry balances without interest, and if you plan wisely, pay them off before the promotional period ends.
This way, you avoid any interest on these purchases while potentially lowering your overall ADB. Pay at least the minimum payment due each month, or the issuer may cancel the promotion. Aim to clear the total balance before the 0% APR period expires to avoid a sudden increase in interest charges.
These promotions can also apply to balance transfers but never to cash advances.
Understanding Your Credit Card Statement
Your credit card statement summarizes your spending and payments. It may look confusing at first, but it shouldn’t take long to sort out. Here’s how to understand some key parts of your statement.
Identify the Average Daily Balance
The average daily balance shows how much you owe on average each day during the billing cycle. You can usually find this near the section that explains interest or in a summary area of your statement.
The ADB helps you see how your daily spending and payments affect your potential interest.
Analyze Interest Charges
Interest charges depend on your ADB and your card’s annual percentage rate (APR). Your statement has a section that breaks down these charges.
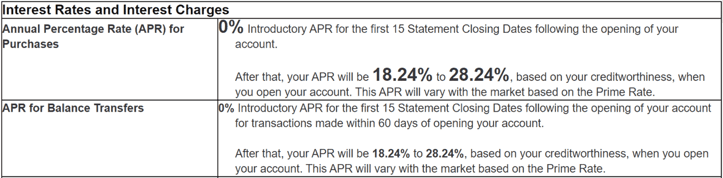
It shows how the issuer calculated the interest you need to pay if you only repay part of the balance by the due date. This section clarifies how a lower balance can reduce your interest charges.
Look for Discrepancies and Errors
Sometimes, mistakes happen. It’s important to act if your ADB or interest charges look wrong or if you see a purchase you don’t recognize. Compare your statement with your own records and contact your credit card company right away if something looks fishy. Doing so can help sort out errors and ensure your statement is correct.
Average Daily Balance and Your Credit Scores
Your average daily balance does more than influence how much credit card interest you pay. It can also affect your credit scores. Here’s how:
The Relationship Between Balance and Credit Utilization
Credit utilization is how much of your credit limit you’re using at any given time, and it’s a major factor in your credit score. Your ADB contributes to your credit utilization ratio because it reflects how much debt you carry on average.
A higher ADB means higher credit utilization, which can lower your credit score.
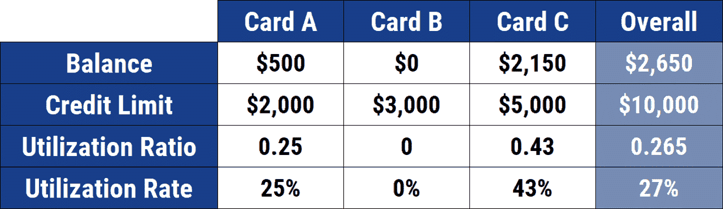
Keeping your credit utilization ratio low (i.e., below 30%) implies that you’re not living beyond your means, which is good for your credit score.
Credit Score Impacts
The average daily balance mostly affects your credit score through how much of your credit you use. However, it can also indirectly impact your credit in a few other ways.
A lower ADB also suggests to lenders that you’re not overdependent on credit. This can make you look better when applying for new credit or loans.
By keeping your ADB low, you may also pay less interest. This saves money, which you can use to pay bills on time or reduce other debts, indirectly boosting your credit score.
Some lenders may consider your ADB when deciding on credit line increases. A lower ADB can show that you manage your money responsibly, making you more creditworthy in the eyes of issuers.
In short, managing your ADB well can encourage good financial habits that improve your overall credit health.
Best Practices for Credit Maintenance
Here are some best practices to help balance your ADB and maintain a healthy credit score:
- Pay off balances frequently: Make multiple smaller payments throughout the month to keep your ADB lower.
- Monitor your charges: Control how much you charge to your credit cards, and don’t let your balance get too high.
- Adjust your credit limits: If you approach your credit limit often, consider asking for a higher limit. Do so only if you’re confident you won’t increase your spending proportionally. A higher credit limit can immediately lower your credit utilization ratio.
- Set balance alerts: Many credit card issuers allow you to set up alerts that let you know when your balance reaches a certain threshold. This can help you keep an eye on your utilization and act quickly if it gets too high.
By following these best practices, you can take more control over your money and work to achieve a higher credit score.
Understand Average Daily Balance to Help Minimize Interest Charges
Your average daily balance is a key factor that impacts how much interest you pay. By keeping your ADB low through frequent payments and careful spending, you can decrease your potential interest charges.
I recommend that you pay your entire balance each month. If that’s a problem, rework your budget to rely less on credit.




![Average Credit Card Debt by Age in [current_year] Average Credit Card Debt by Age in [current_year]](https://www.cardrates.com/images/uploads/2023/05/CR-AverageCreditCardDebtbyAge.jpg?width=158&height=120&fit=crop)
![Average Credit Card Debt by State in [current_year] Average Credit Card Debt by State in [current_year]](https://www.cardrates.com/images/uploads/2023/06/CR-AverageCreditCardDebtbyState-1250X650.jpg?width=158&height=120&fit=crop)

![Average Credit Card Debt by Country in [current_year] Average Credit Card Debt by Country in [current_year]](https://www.cardrates.com/images/uploads/2023/06/CR-AverageCreditCardDebtbyCountry-1250X650.jpg?width=158&height=120&fit=crop)
![Average Credit Card Debt in America in [current_year] Average Credit Card Debt in America in [current_year]](https://www.cardrates.com/images/uploads/2023/06/CR-AverageCreditCardDebtInAmerica-1250X650.jpg?width=158&height=120&fit=crop)